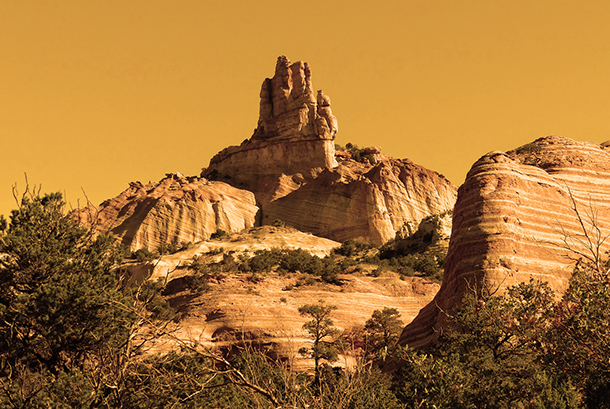
IMAGE: The imposing and stunning sight of Church Rock in the Navajo Nation, located in northwestern New Mexico.
Here is the true cost of the American empire.
In 1945, the first atomic bomb was tested at the U.S. defense facility at Alamogordo, New Mexico. Just 34 years later, the area also suffered the worst nuclear waste disaster in its history – which did not receive nearly as much media and political attention than other high-profile incidents. And there is a reason for this.
On July 16, 1979, at the Church Rock uranium mines, occurred the worst spill of radioactivity release to our environment in the history of the nuclear industry. The radiation is invisible to this day, still devastating communities living along the Puerco River in northwestern New Mexico. There you will witness the devastation wrought on residents, including high levels of cancer, as well as the impact of other toxic substances left-over from the Church Rock disaster.
In the words of Larry King, an underground surveyor at the United Nuclear Corporation’s Church Rock Uranium mine in New Mexico, “Three Mile Island had more coverage and people were compensated right away.” He added, “I always say we don’t get the same attention because we live in impoverished native community… We live in a sacrifice zone.”
After 40 years, the problem still persists, and appears to much larger than previously thought.
Writer Samuel Gilbert from Vice News reports…
Early in the summer of 1979, Larry King, an underground surveyor at the United Nuclear Corporation’s Church Rock Uranium mine in New Mexico, began noticing something unusual when looking at the south side of the tailings dam. That massive earthen wall was responsible for holding back thousands of tons of toxic water and waste produced by the mine and the nearby mill that extracted uranium from raw ore. And as King saw, there were “fist-sized cracks” developing in that wall. He measured them, reported them to his supervisors, and didn’t think anything more of it.
A few weeks later, at 5:30 a.m. on July 16, 1979, the dam failed, releasing 1,100 tons of uranium waste and 94 million gallons of radioactive water into the Rio Puerco and through Navajo lands, a toxic flood that had devastating consequences on the surrounding area.
“The water, filled with acids from the milling process, twisted a metal culvert in the Puerco,” according to Judy Pasternak’s book Yellow Dirt: A Poisoned Land and the Betrayal of the Navajos. “Sheep keeled over and died, and crops curdled along the banks. The surge of radiation was detected as far away as Sanders, Arizona, fifty miles downstream.” According to a Nuclear Regulatory Commission report, radioactivity levels in the Puerco near the breached dam were 7,000 times that of what is allowed in drinking water.
The heavily contaminated water flowed over the river banks, creating radioactive pools. “There were children up and down the river playing in those stagnant pools, and they were deadly poisonous,” Jorge Winterer, a doctor with Indian Health Service in Gallup, New Mexico, said after the spill.
Earlier this year, standing in his yard next to an old Chevy, King pointed in the direction of the now dry Rio Puerco. “It came right through there,” said King. The unleashed river of waste had flowed through his family’s land just a half-mile from his house. “I remember the terrible odor and the yellowish color of the water.” He recalls seeing an elderly woman who had burned her feet crossing the Puerco while watering her sheep that day.
King still lives on the family land, two miles downstream of the rebuilt dam in the Church Rock chapter of the Navajo Nation. His home is surrounded by a beautiful, unforgiving landscape of red rock cliffs, a scattering of Navajo residences and, if you look closely, fencelines with KEEP OUT signs marking the numerous abandoned uranium sites.
Forty years later, the Church Rock spill remains the largest single largest accidental release of radioactivity in U.S. history, worse in terms of total radiation than that of the partial meltdown at Three Mile Island and second in world history only to the 1986 Chernobyl catastrophe, both of which have loomed much larger in the cultural imagination. The effects of the spill have lingered for an entire generation: In 2007, the Church Rock Uranium Mining Project found widespread contamination of drinking water sources in the Church Rock area.
Navajo residents say they have not been given the attention given to other victims of nuclear accidents, even as they remain under the catastrophe’s long shadow, dealing with poisoned livestock and ongoing health problems amid other aftereffects. “We have never been a priority,” said King. “Forty years after the spill and nothing has been done.”
“Our generation is afraid of having children,” said Faith Baldwin, who grew up on the Navajo nation surrounded by abandoned uranium mines. “Cancer runs in our family but it shouldn’t. Cancer, diabetes were nonexistent in Navajo rez.”
(…) For many residents, the spill has come to embody the broader toxic legacy of the uranium industry on the indigenous lands of the West. According to the EPA, there are over 500 abandoned uranium mines, mill sites, and waste piles on Navajo Nation land that continue to contaminate water, soil, livestock and housing.
“The Church Rock spill symbolizes the governmental and societal indifference to the impacts of uranium development on Indigenous lands,” said Jantz. “The Church Rock spill is the third largest nuclear accident after Fukushima and Chernobyl, and the largest in the US in terms of radiation released, but nobody knows about it.”
Continue this story at Vice News
READ MORE NUCLEAR NEWS: 21st Century Wire Nuclear Files
SUPPORT OUR MEDIA PLATFORM – BECOME A MEMBER @21WIRE.TV